Have you ever wondered how doctors and other healthcare professionals keep accurate records about their patients? They use two important tools: medical dictation and medical transcription. Understanding medical dictation and medical transcription can be challenging, but it’s important to learn the basics. These two terms may sound similar, but they serve different purposes in the healthcare field.
Let’s explore what medical dictation and transcription are, how they work, and how they differ from each other.
What is Medical Dictation?
Medical dictation is when doctors or other healthcare providers speak out loud to record important information about a patient. Imagine a doctor checking a patient and then talking into a recorder or microphone, saying things like, “Patient John has a fever, sore throat, and needs antibiotics.” This spoken information is stored as an audio file.
Dictation helps doctors save time because they don’t have to stop and write things down. Instead, they can just speak while they focus on their patients.
Medical Dictation is like taking voice notes. It is fast and easy for doctors but needs someone to turn those spoken words into written text, which is where transcription comes in.

What is Medical Transcription?
Medical transcription is the process of turning the spoken words from dictation into written documents. Transcriptionists listen to the audio recordings and type out exactly what was said, making sure that every detail is captured correctly.
These written records are important because they are used in a patient’s medical history, treatment plans, and other important documents. For instance, when a doctor dictates a diagnosis or a treatment plan, the transcriptionist makes sure that information is correctly documented in the patient’s medical file.
A study revealed that error rates in traditional medical transcription can be as high as 11%, with mistakes in medical terminology being a key contributor. These errors highlight the importance of modern solutions like AI-assisted transcription for accuracy.

How Does Medical Dictation Work?
Medical dictation works by using technology like digital recorders, smartphones, or special dictation software. Here’s how it usually happens:
- Recording: The doctor speaks into a device, capturing their thoughts and observations about the patient.
- Saving the File: The spoken words are saved as an audio file, often in formats like MP3 or WAV.
- Storage: These audio files are stored in a secure system, which might be on the doctor’s computer, a cloud service, or a hospital’s database.
This whole process helps doctors document patient information quickly and efficiently.
How Does Medical Transcription Work?
Medical transcription takes the recorded dictation and converts it into written text. Here’s how it works step by step:
- Listening: A transcriptionist listens to the audio recording.
- Typing: They type out what the doctor has said, making sure to include all important details.
- Editing and Proofreading: The transcriptionist reviews the typed document for accuracy, checking for mistakes in spelling, grammar, or medical terminology.
- Finalizing: The final document is then saved in the patient’s medical record for future reference.
Some modern systems use speech recognition software to help with transcription, but humans still play a big role in ensuring everything is accurate.
Get a detailed overview from our previous blog on Complete Guide on Medical Dictation and Transcription 2024.
Differences Between Medical Dictation and Medical Transcription
Although dictation and transcription often work together, they are different processes with unique roles:
- Purpose:
- Dictation: Involves speaking and recording information. It’s a way for doctors to quickly capture what they’re thinking without having to write it down.
- Transcription: Involves listening and writing. It turns the spoken words from dictation into a written document that can be saved, shared, and referred to later.
- Technology:
- Dictation: Uses recording devices like smartphones, digital recorders, or specialized dictation software.
- Transcription: Uses headphones, a computer, and sometimes software like speech recognition tools that help convert audio to text.
- People Involved:
- Dictation: Usually just the doctor or healthcare provider speaking into a device.
- Transcription: Involves transcriptionists who listen, type, and edit the dictation into readable text.
- Speed and Accuracy:
- Dictation: Quick and easy but relies on someone else to do the transcription accurately.
- Transcription: Slower because it requires careful listening and typing, but it ensures that the information is correctly documented.
Why Are Both Dictation and Transcription Important?
Both processes are essential in healthcare because they ensure that all patient information is captured and recorded accurately. Here are a few reasons why they are so important:
- Saving Time: Dictation helps doctors save time during patient visits. They don’t have to stop and write everything down—they just talk and keep going.
- Accuracy in Records: Transcription makes sure that all the doctor’s notes are clear, well-documented, and saved for future use. This is critical for patient care because it ensures that all details are correctly noted and can be accessed when needed.
- Better Patient Care: By accurately recording and transcribing medical information, doctors can make informed decisions, and other healthcare providers can easily access a patient’s history, medications, and treatment plans.
- Legal Documentation: Medical records are legal documents, so it’s important that they are accurate and complete. Errors or missing information could cause problems in treatment or legal issues.

Challenges Faced in Dictation and Transcription
Even though medical dictation and transcription make life easier for healthcare providers, they are not without challenges:
- Dictation Quality: Sometimes, doctors speak too quickly, mumble, or use complex medical terms that are hard to understand. This can make transcription difficult.
- Errors in Transcription: Mistakes in transcription can occur, especially if the audio quality is poor or if the transcriptionist is not familiar with medical terminology. Errors can lead to misunderstandings and mistakes in patient care.
- Technology Dependence: Both dictation and transcription rely heavily on technology. If the devices or software fail, it can disrupt the process, leading to delays.

Modern Solutions: Speech Recognition Technology
To reduce errors and speed up the transcription process, many healthcare providers now use speech recognition software. This technology automatically converts spoken words into text without needing a human transcriptionist. However, even with this advanced technology, human review is still necessary to ensure accuracy because the software can misinterpret words, especially those that sound similar but have different meanings.
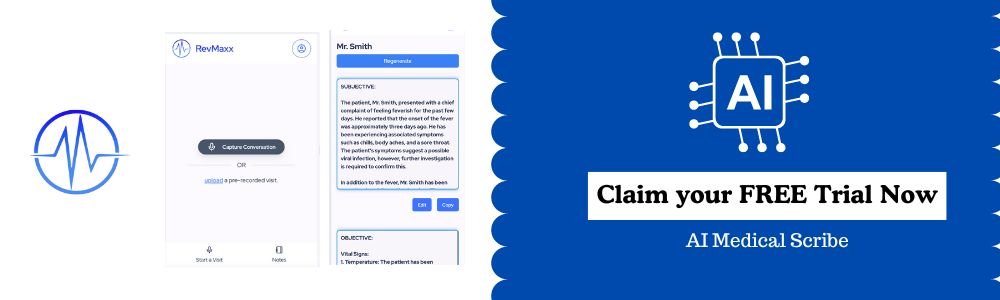
How Can RevMaxx Help in Medical Dictation and Transcription?
RevMaxx AI Medical Scribe simplifies the process of medical dictation and transcription, making life easier for healthcare professionals. With our AI medical scribe, we turn spoken medical notes into accurate, well-formatted text accurately.
This helps doctors spend less time on paperwork and more time caring for patients. Our speech recognition technology captures every detail of a doctor’s dictation, ensuring complete and error-free patient records.
RevMaxx also provides customizable features that fit seamlessly into any healthcare setting, allowing doctors to dictate using their preferred devices. Our secure platform ensures patient data remains private, meeting HIPAA compliance standards.

Conclusion
There is no surprise that medical dictation and transcription are key processes in healthcare that work hand-in-hand to capture and record patient information.
Dictation involves speaking and recording, while transcription involves listening and converting that speech into text. Both are essential for maintaining accurate medical records, improving patient care, and saving time for healthcare providers.
Understanding the difference between these two processes helps us appreciate the important roles they play in the medical field.









